Hot sale good quality Precision Casting Wax to moldova Factories
Short Description:
Product Detail
Product Tags
Hot sale good quality Precision Casting Wax to moldova Factories Detail:
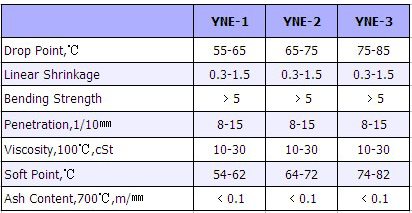
Precision Casting Wax mainly is used for precision mechanical process with zero allowance or very limited allowance. We can not adopt general casting technique, but can only adopt zero allowance casting or precision casting. Because of the product’s structure is very delicate and complex especially in bejeweled with golden and silver, such as diamond ring, brooch, earring etc.
The characteristics of precision casting wax are: good coating property, no denaturalization to be heated, good flow ability, good thermal stability, and well surface finish.
Product detail pictures:

We continuously execute our spirit of ''Innovation bringing development, Highly-quality ensuring subsistence, Management advertising and marketing gain, Credit history attracting buyers for Hot sale good quality Precision Casting Wax to moldova Factories, The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Zambia , Angola , Durban , We pay high attention to customer service, and cherish every customer. We have maintained a strong reputation in the industry for many years. We are honest and work on building a long-term relationship with our customers.
ESP8266 Controlled Car / RC Bot (WiFi Internet-of-Things IoT)
I have created RC Car using ESP8266 and Android mobile.
This is my first Project with ESP8266 ESP-12 (NodeMcu Lua).
Spend it up for y’all. Hope you like it.
Big Thanks to RoboRemo apps creator.
Required:
1. ESP8266 ESP-12 (NodeMcu Lua)
2. Dual H Bridge DC Motor Drive Controller Board Module – L298N D2
3. 12v Battery [Im using 3*(18650 3.7v 6000mAh Batteries)]
4. 4 Geared DC Motor
5. Frame for Holding 4 DC Motors.
6. Any Android Mobile.
Please comment If you need any help.
Or drop me mail : shirishyc@gmail.com
Microchannel Plate Detector MCP-MA25/2 sales@dmphotonics.com
Featured Research:
View online: https://jcp.aip.org/resource/1/jcpsa6/v138/i17/p174310_s1?isAuthorized=no&ver=pdfcov
Spectroscopic observation of gold-dicarbide: Photodetachment and velocity map imaging of the AuC2 anion
Photoelectron spectra following photodetachment of the gold dicarbide anion, AuC−
2 , have been recorded using the velocity map imaging technique at several excitation wavelengths. The binding energy spectra show well-defined vibrational structure which, with the aid of computational calculations and Franck-Condon simulations, was assigned to a progression in the Au–C stretching mode, ν3. The experimental data indicate that the features in the spectrum correspond to a 2A←3A transition, involving states which we calculate to have bond angles ∼147◦ but with a low barrier to linearity.
EXPERIMENTAL METHOD
Since the specific apparatus used for these experiments has not been previously published, a detailed description is given here. Experiments were performed under high vacuum conditions within a two chamber, differentially pumped system operated at pressures of 1 × 10^−4 and 1 × 10^−6 mbar, respectively. Gold-carbide clusters were produced within a Smalley-type laser ablation source modelled on our existing designs. The source was operated with benzene seeded in helium gas to produce the metal-carbon products. The clusters exit the source and expand towards a two stage Wiley-
McLaren type time of flight where anion species are pulse extracted orthogonally into a drift region. Ion optics corrects the flight path of the extracted anions so that they enter the VMI electrodes positioned immediately after the drift region. The geometry of the time of flight electrodes was designed such that the second order space focus was coincident with the photodetachment point within the VMI electrodes.25 At this point, the ion packets of the clusters were condensed to small volumes and separated in time according to their mass to charge ratio, m/e. Individual m/e species are probed by varying the photodetachment timing. A removable (via a linear motion feed-through), dual micro-channel plate detector (MCP, Del Mar Ventures, Del Mar Photonics MCP-MA25/2) is located immediately after the VMI electrodes to provide mass spectral identification
of cluster species for photodetachment. The velocity map imaging electrodes were pulsed to highvoltage 200 ns prior to the photodetachment event to ensure
stable potentials. Photodetachment was performed via laser light produced by a dye laser pumped by the second harmonic of a Nd:YAG laser. The incident laser power was varied in order to keep the number of detected electrons at a rate of ∼1 per laser pulse, but was typically on the order of a few microjoules at the point of entry into the chamber. To prevent deflection of the photodetached electrons by stray magnetic fields, the detection chamber was lined with magnetic shielding (Co-Netic 0.36 mm thickness, Magnetic Shield Corp.).
Research interests lay in the fields of laser chemistry and reaction dynamics, and include the following themes:
Reaction Dynamics:
Energy partitioning during photodissociation of van der Waals molecules.
Evaporation dynamics at the liquid-vacuum interface.
Electronic Spectroscopy:
Structure of van der Waals clusters.
2-Dimensional Laser Induced Fluorescence (2D-LIF) spectroscopy.
Rovibronic analysis of large polyatomic molecules.
Nanotechnology:
Nanoparticle formation using laser based methods.
Molecular spectroscopy
Reaction dynamics
https://www.dmphotonics.com/MCP_MCPImageIntensifiers/mcpma252.htm
photodetachment cross section
photodetachment spectroscopy
photodetachment of electrons