Massive Selection for U-1A00 thermal wax actuator for thermostatic automatic water drain valve for Brazil Manufacturers
Short Description:
Product Detail
Product Tags
Massive Selection for U-1A00 thermal wax actuator for thermostatic automatic water drain valve for Brazil Manufacturers Detail:
1. Operation Principle
The Thermostatic Wax that has been sealed in shell body induces expansion by a given temperature, and inner rubber seal part drives its handspike to move under expansion pressure to realize a transition from thermal energy into mechanical energy. The Thermostatic Wax brings an upward movement to its handspike, and automatic control of various function are realized by use of upward movement of handspike. The return of handspike is accomplished by negative load in a given returned temperature.
2. Characteristic
(1)Small body size, occupied limited space, and its size and structure may be designed in according to the location where needs to work.
(2)Temperature control is reliable and nicety
(3)No shaking and tranquilization in working condition.
(4)The element doesn’t need special maintenance.
(5)Working life is long.
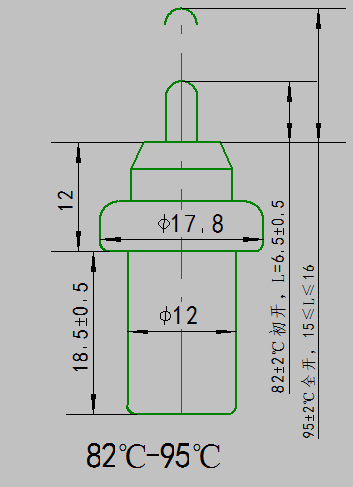
3.Main Technical Parameters
(1)Handspike’s height may be confirmed by drawing and technical parameters
(2)Handspike movement is relatives to the temperature range of the element, and the effective distance range is from 1.5mm to 20 mm.
(3)Temperature control range of thermal wax actuator is between –20 ~ 230℃.
(4)Lag phenomenon is generally 1 ~ 2℃. Friction of each component part and lag of the component part temperature cause a lag phenomenon. Because there is a difference between up and down curve of traveling distance.
(5)Loading force of thermal wax actuator is difference, it depends on its’ shell size.
Product detail pictures:

We stay with our company spirit of "Quality, Performance, Innovation and Integrity". We goal to create more value for our clients with our abundant resources, advanced machinery, experienced workers and superb solutions for Massive Selection for U-1A00 thermal wax actuator for thermostatic automatic water drain valve for Brazil Manufacturers, The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Monaco , Mecca , Paris , By integrating manufacturing with foreign trade sectors, we can offer total customer solutions by guaranteeing the delivery of right items to the right place at the right time, which is supported by our abundant experiences, powerful production capability, consistent quality, diversified product portfolios and the control of the industry trend as well as our mature before and after sales services. We'd like to share our ideas with you and welcome your comments and questions.
The idle control valve adjusts the engine rev’s for a cold start and on later models adjusts the idle when the engine is warmed up. The oxygen sensor relays to the ECU for your correct fuel mixture, this is just removal and cleaning as part of vehicle maintenance.
The FAMCO LH Plastic Wall Vents are made of high density polyethylene plastic (HDP) for durability and longevity. They have UV inhibitors for greater stability in all weather conditions, a full 1″ collar for secure pipe attachment and heavy duty borders for secure and durable mounting. The LH has movable louvers and is used for exhaust, dryer and bathroom exhaust vents. Available in brown and white.
Please go to the following link to purchase yours today!…
https://www.famcomfg.com/wall-vents/plastic-wall-vent-with-movable-louvers.html