15 Years Factory wholesale Special Wax in Agriculture and Forestry Wholesale to Madrid
Short Description:
Product Detail
Product Tags
15 Years Factory wholesale Special Wax in Agriculture and Forestry Wholesale to Madrid Detail:
(1)YNE4 Series Special Molding Moisturized Wax for Fruit Trees
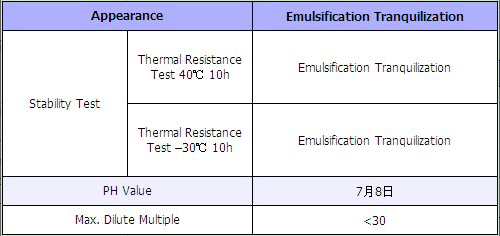
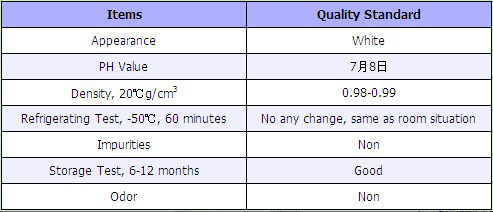
In order to protect fruit trees and shrubs from desiccation during winter dormancy or transportation or to keep moisture in summer drought, Special Molding Moisturized Wax is spayed on the surface of trees, forming the protecting film in surface of trees. The film has some adequate micro pore that could efficiently reduce the losses of moisture in the surface of the trees, and it simultaneously ensures physiological respiration of the trees.
(2) YNE5 Series Special Preventing Frostbite Wax for Trees
(3) In large northern areas of our country, the winter season is severe cold and the spring season is more heavy windy.
The early winter and the late spring’s frost are quite disadvantage to young plant, the weather is particularly abnormal coldness after spring comes, and frequently injures these trees. As a result young plant is cold death. YNE5 Series Special Preventing Frostbite Wax for Trees not only has anti-freezing effect on trees but also well effect on anti-sprouting etc. Spraying on branches and leaves of trees can make exuberant growth of foliage.
Product detail pictures:

We're commitment to offer you the aggressive cost ,superb products and solutions top quality, too as fast delivery for 15 Years Factory wholesale Special Wax in Agriculture and Forestry Wholesale to Madrid, The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Niger , azerbaijan , Iceland , It using the world's leading system for reliable operation, a low failure rate, it suitable for Argentina customers choice. Our company is situated within the national civilized cities, the traffic is very convenient, unique geographical and economic conditions. We pursue a people-oriented, meticulous manufacturing, brainstorm, build brilliant" business philosophy. Strict quality management, perfect service, reasonable price in Argentina is our stand on the premise of competition. If necessary, welcome to contact us by our website or phone consultation, we'll be happy to serve you.
This is one of the available climate control panels for your vehicle. If your vehicle is equipped with a different climate control system, see your Owner’s Manual for additional information.
The Auto mode may be used all year round. The system automatically regulates and maintains fan speed, airflow and temperature in the cabin. To turn the system ON, press the AUTO button. The indicator light turns ON when the system is activated.
Pressing the DEFROST button or changing the fan speed or airflow mode turns off the AUTO function and switches the system to manual control. To reactivate automatic control, press the AUTO button.
To turn the entire climate control system OFF, press the OFF button.
Your vehicle has separate temperature control buttons for the driver and front seat passenger. Turn the driver’s side control knob to the right for warmer or left for a cooler temperature.
If you want to adjust the passenger side temperature independently from the driver’s side, press the DUAL button or turn the temperature control knob left or right. The DUAL control indicator and the passenger’s side temperature will be displayed on the monitor.
If the DUAL mode is not active, the driver’s temperature control buttons set the temperature for both the driver and passenger. To switch back to driver control when the DUAL mode is active, press the DUAL button again.
Press the air flow control button repeatedly to cycle through these four air flow choices:
• Air will flow from the center and side vents
• Air will flow from center, and side and foot outlets
• Air will flow from mainly foot outlets
• Air will flow from the defroster and foot outlets
The selected air flow mode is displayed on the monitor.
Press the A/C button to manually turn the air conditioning ON or OFF.
Intake air control is automatically regulated in AUTO mode. Press the intake air control button to manually alternate between recirculating inside air and drawing outside air into the cabin.
The indicator light on the button will illuminate when the recirculating mode is active.
The air recirculation mode increases air conditioning efficiency and helps block outside odors from entering the cabin.
To return to automatic control of the air intake mode, press and hold the air intake control button for approximately 2 seconds until the indicator light flashes twice.
Use the fan speed control buttons to adjust the fan speed. Press this button to increase fan speed. Press this button to decrease fan speed. When you manually change fan speeds, it turns off the automatic climate control mode. To return to automatic climate control, press the AUTO button.
To defrost or defog the front and side windows, press the DEFROST button. The indicator light will illuminate. Airflow will be directed to the front and side windows.
In the DEFROST mode, the Air Conditioner activates automatically at temperatures above 23 degrees Fahrenheit and the air recirculate mode automatically turns off, allowing outside air to be drawn into the passenger compartment to improve the defogging and deicing performance. For windshield deicing, the temperature and fan speed should be at the highest settings.
To defrost or defog the rear window and the outside mirrors, push the REAR WINDOW DEFROSTER switch. The indicator light will illuminate. After defrosting, push the switch again to turn OFF. If not turned OFF manually, this feature will automatically deactivate after a period of time.
There is a temperature sensor located on top of the dashboard near the windshield that helps regulate the automatic climate control settings. Keep this area clear of papers and other materials.
For the comfort of your rear passengers, your vehicle is equipped with rear climate controls.
To control the rear automatic air conditioning system with the front air conditioner control, press the REAR button. When the rear automatic air conditioner control is turned on, the indicator light on the rear button illuminates and the front display screen switches to the REAR AIR-CONDITIONING screen.
Press the REAR button again and the REAR AIR-CONDITIONING screen will no longer be visible. The REAR button will remain illuminated and the rear passengers will then have control of the rear climate controls.
These are the rear climate controls. Press the up or down fan buttons to control the fan speed. A comfortable temperature can be selected by locating the TEMP button and pressing the arrows either up or down for warmer or cooler temperatures.
Press the MODE button to change the airflow mode.
The AUTO button on the rear climate controls puts the system in AUTO mode, which automatically regulates the settings for the rear cabin based on the set temperature. The AUTO mode is disabled if the rear passengers manually increase or decrease the fan speed.
Press the OFF button to turn off the rear climate controls.
A short video to explain the basics of the setup in its standard mode. As you can see everything is up and running! I still have to alter the sketch to incorporate the RTC to control the lighting cycle though.
After shooting the video I checked the settings in the sketch and the Hot end temperature was actually set to trigger at 88F (hence why it kicks back in so quickly) and the Cool end at 83F.